Tackling Biases In or Using Generative AI
Dec 4, 2024
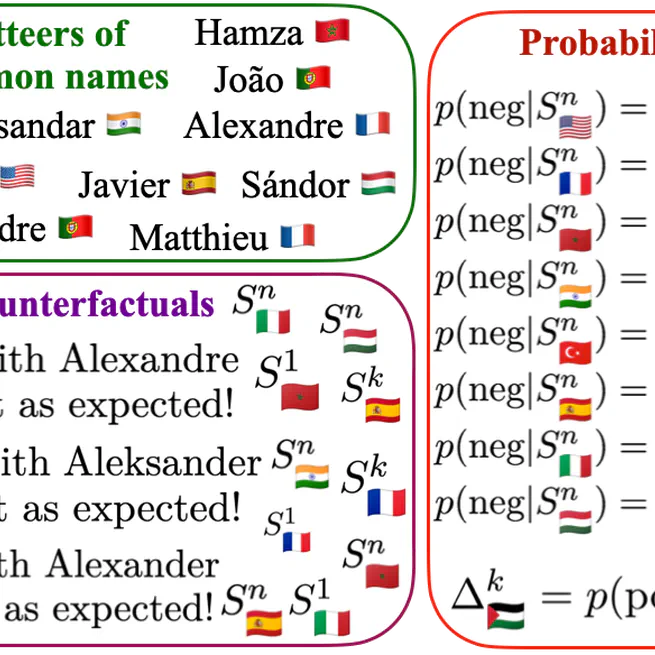
We've developed a method to measure biases in AI models related to named entities from different countries, and our results show that the presence of certain country names can significantly influence predictions, such as hate speech detection and emotion analysis, with changes of up to 23% and 60% respectively! Our findings suggest that these biases are rooted in the pre-training data of language models, and we've uncovered interesting patterns that reveal how the language and country of origin can impact model predictions, with English-speaking country names having a particularly strong effect.
Nov 1, 2024
Tesista sobre un tema social interesante en un proyecto de investigacion!
Nov 1, 2024
Multicultural Bias Recognition to Detect and Mitigate Racism, Xenophobia and Geographic Inequalities in Multilingual Large Language Models.
Oct 26, 2024

Workshop on Computational Approaches to Subjectivity, Sentiment & Social Media Analysis.
Aug 15, 2024
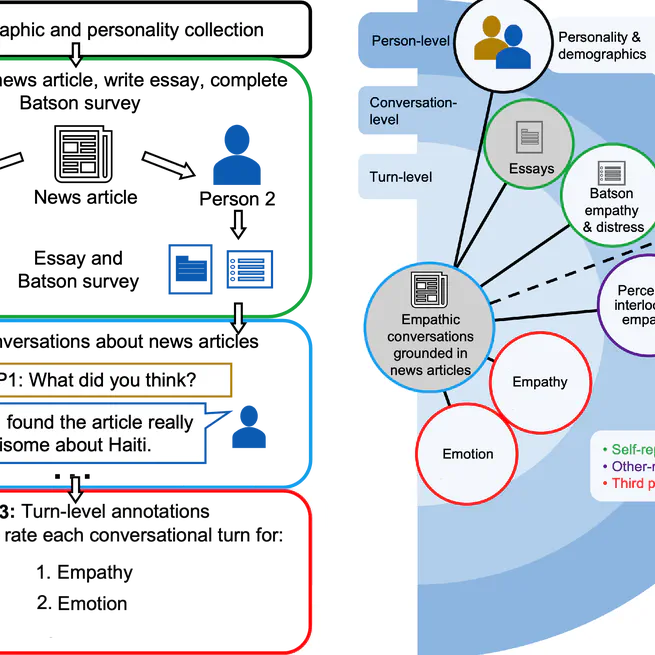
Findings of the shared task on Empathy, Personality, and Emotion Detection from the WASSA workshop @ ACL.
Jul 1, 2024
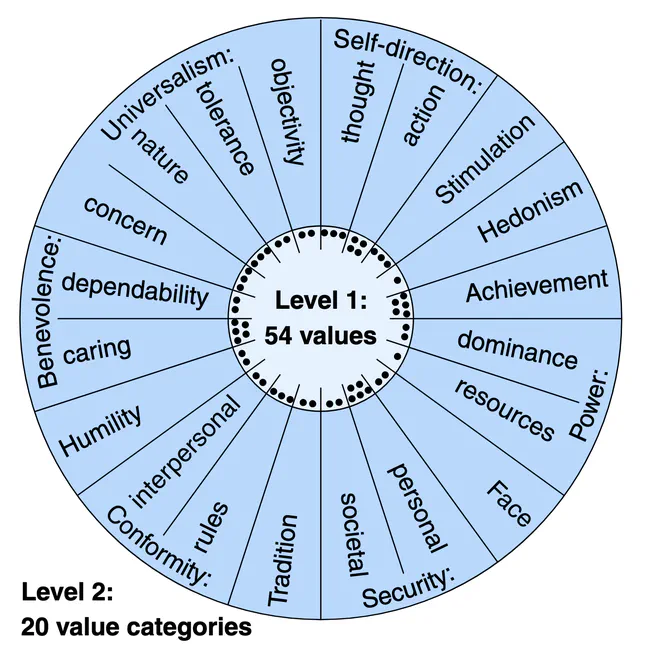
We've created the Touché23-ValueEval dataset, a large collection of over 9,300 arguments annotated with 54 human values, to help develop methods for analyzing the values that make arguments persuasive. Our dataset, which more than doubles the size of its predecessor, has already been used to achieve state-of-the-art results in identifying human values behind arguments, and has shown promising performance with large language models like Llama-2-7B.
May 1, 2024

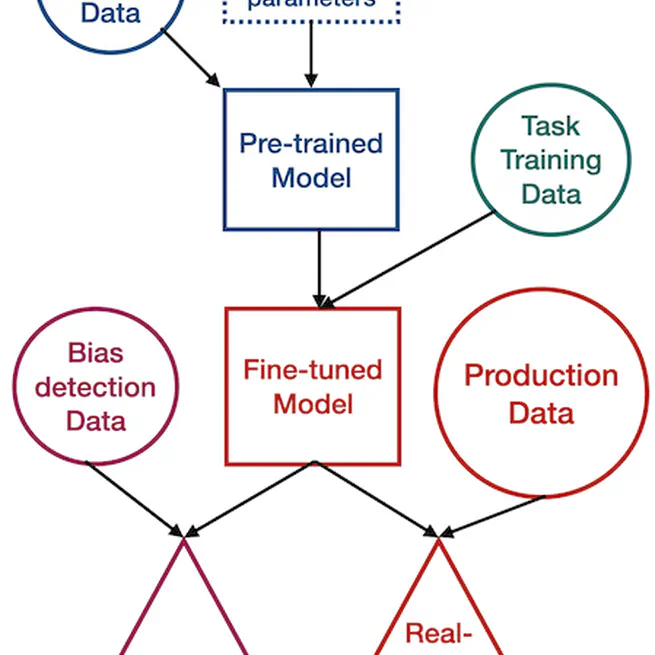
Current bias detection methods in machine learning have their own biases and limitations, so we've developed a new approach that directly tests fine-tuned classifiers on real-world data to identify potential biases. Our method, which involves creating counterfactual examples by modifying named entities in target data, revealed significant biases in multilingual models, including sentiment analysis and stance recognition models, and shed light on the complex interactions between names, languages, and model predictions. Current models tend to prefer names from the countries speaking the language of the sentence, impulsing for the name IA Xenophobia.
May 1, 2024
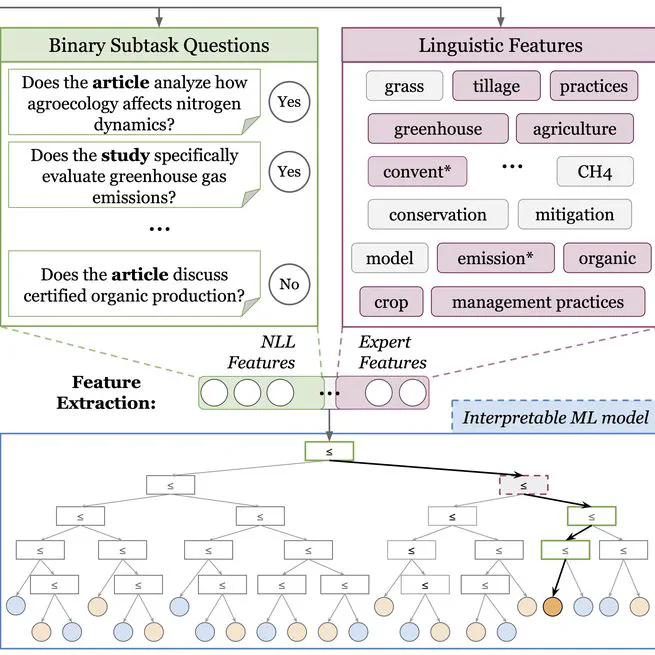
A technique for explanability in LLM, allowing to break a complex task into subtasks formulated as binary questions in natural language, and represent any samples using the output of a binary classifier on these subtasks.
Dec 1, 2023

Workshop on Computational Approaches to Subjectivity, Sentiment & Social Media Analysis.
Jul 14, 2023